문제
Given the root of a binary search tree and the lowest and highest boundaries as low and high, trim the tree so that all its elements lies in [low, high]. Trimming the tree should not change the relative structure of the elements that will remain in the tree (i.e., any node’s descendant should remain a descendant). It can be proven that there is a unique answer.
Return the root of the trimmed binary search tree. Note that the root may change depending on the given bounds.
제한사항
입출력 예
![example]()
1
2
3
4
| Example 1:
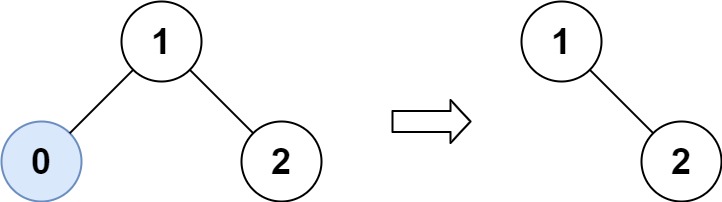
Input: root = [1,0,2], low = 1, high = 2
Output: [1,null,2]
|
![example]()
1
2
3
4
| Example 2:
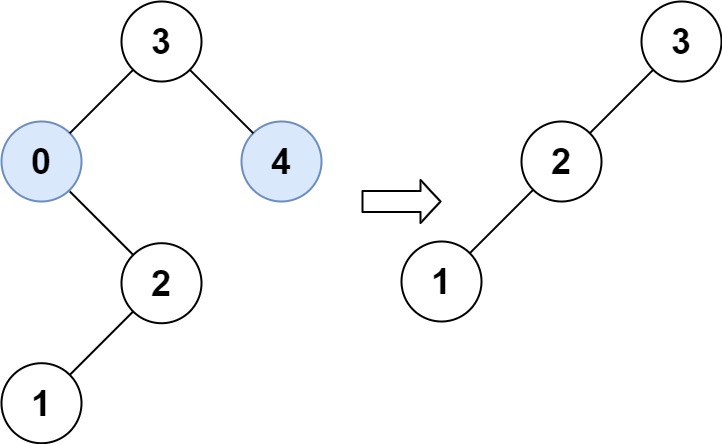
Input: root = [3,0,4,null,2,null,null,1], low = 1, high = 3
Output: [3,2,null,1]
|
1
2
3
4
| Example 3:
Input: root = [1], low = 1, high = 2
Output: [1]
|
1
2
3
4
| Example 4:
Input: root = [1,null,2], low = 1, high = 3
Output: [1,null,2]
|
1
2
3
4
5
| Example 5:
Input: root = [1,null,2], low = 2, high = 4
Output: [2]
|
풀이
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
| /**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* trimBST(TreeNode* root, int low, int high) {
if (root == nullptr) {
return nullptr;
}
if (root->val < low) {
return trimBST(root->right, low, high);
}
if (root->val > high) {
return trimBST(root->left, low, high);
}
root->left = trimBST(root->left, low, high);
root->right = trimBST(root->right, low, high);
return root;
}
};
|